Problem 9
Compound A, a solid, C9H8O2 effervesces when added to a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate). It reacts immediately with bromine water, decolourising it, with the product being B, C9H8O2Br2. With aqueous sodium hydroxide solution B gives the sodium salt of C, C9H10O4; this compound can be oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate solution to D C9H6O4. D reacts with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine but not with ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. D gives steamy fumes with phosphorus pentachloride, the organic product being E, C9H5O3Cl.
With ammonia E gives F, C9H7O3N.
Both G and A are oxidised by hot aqueous potassium manganate(VII) solution to the sodium salt of G, C7H6O2.
Identify compounds A to G, explaining all the observations as fully as possible.
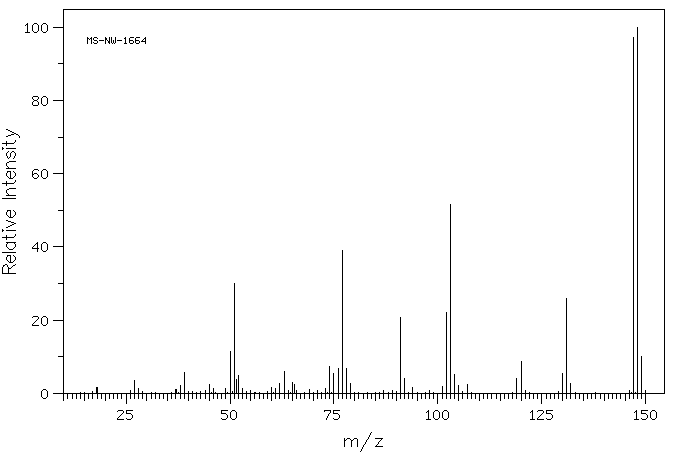
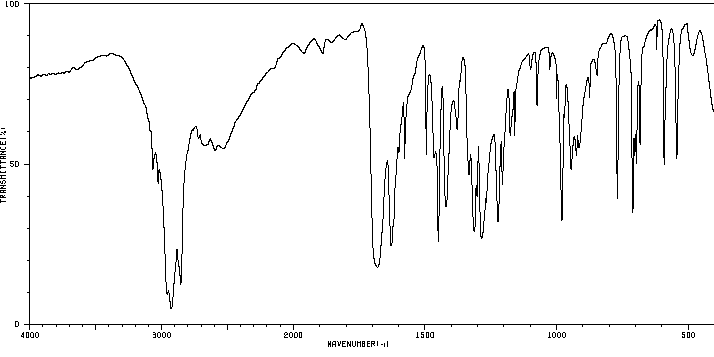
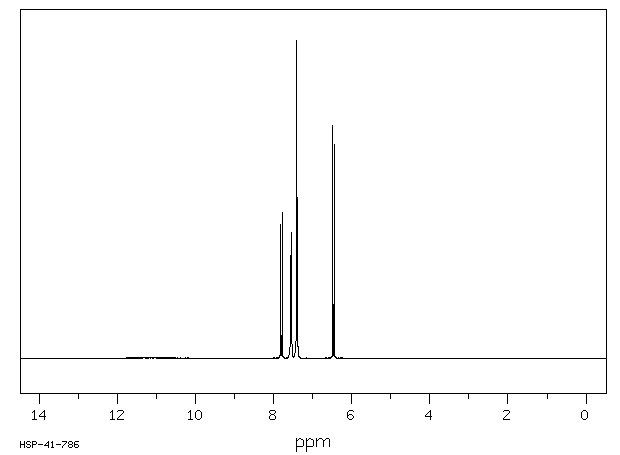
The MS, IR and NMR spectra of A are given below; make what deductions you can from these spectra.
Mass spectrum:

Infrared spectrum: Nujol mull. The Nujol mullis a technique where a solid is ground tp a paste with Nujol, which is a paraffin oil. The spectrum of Nujol is superimposed on the spectrum of the compound.
Proton NMR spectrum: (this is not required in the current Edexcel syllabus).
Answer 9 Organic problems contents Home page