 |
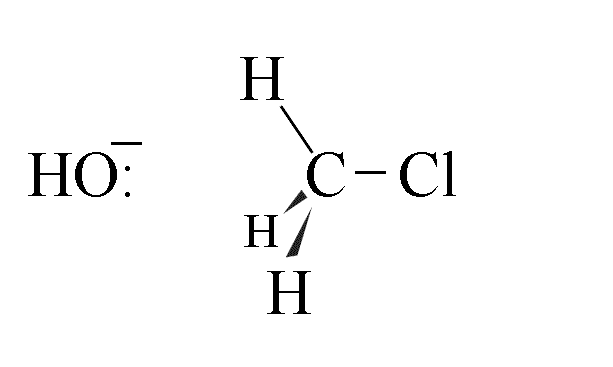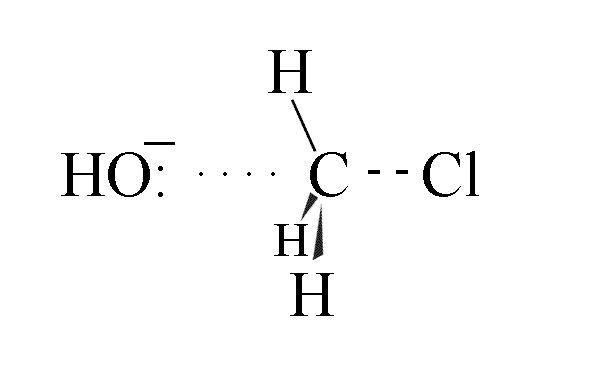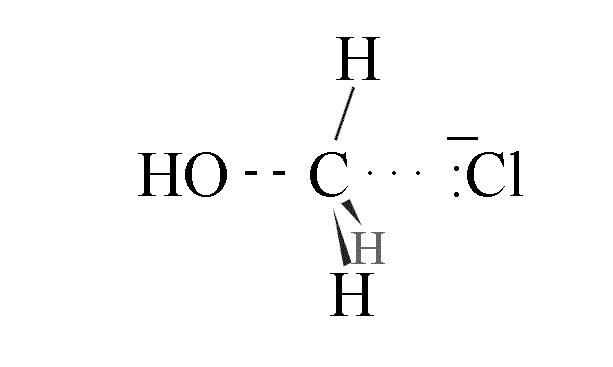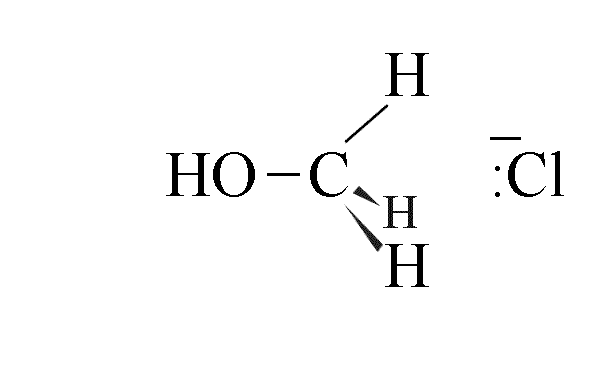
- The hydroxide ion approaches the chloromethane molecule along the path of lowest energy,
which is colinear with the C-Cl axis
- As the C-O bond starts to form, the C-Cl bond starts to break
- The highest energy transition state has partial bonds between the C-O and the C-Cl
- The C-O bond shortens and srtrengthens as the C-Cl bond lengthens and weakens
- The final product is one where the configuration of the carbon atoms has inverted; use
of a chiral halogenoalkane leads to an inversion of configuration, called the Walden
Inversion
|

